mitopoiesi chanel | Mitochondrial channels: ion fluxes and more mitopoiesi chanel Therefore, the discovery of mitochondrial ion channels influencing ion permeability through the membrane has defined a new dimension of the function of ion channels in different cell types, . Lai palīdzētu Elektrum klientiem paaugstināt komforta līmeni, ko sniedz elektroenerģijas lietošanā ikdienā, piedāvājam projektu Energo pulss. Tas būs palīgs klientiem, lai izvērtētu, cik efektīvi mājoklī tiek lietoti enerģijas resursi, salīdzinot līdzīgu mājsaimniecību enerģijas patēriņu, kā arī sniegs praktiskus .Elektrība jūsu ierīcēm, dabasgāze siltumam un virtuvei, saules paneļi un apkures risinājumi mājoklim, elektroauto uzlādes stacijas, energorisku apdrošināšana sirdsmieram. Ar mums piemērotākā produkta izvēle ir viegla, rēķinu apmaksa un .
0 · The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel
1 · The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel
2 · Mitochondrial channels: ion fluxes and more
3 · Mitochondrial Ion Channels: Gatekeepers of Life and Death
4 · Mitochondrial Ion Channels of the Inner Membrane and Their
5 · Mitochondrial Ion Channels
6 · Ion Channels and the Electrical Properties of Membranes
7 · Introduction to the Theme on Membrane Channels
8 · Identification of an ATP
9 · 11.3: Diffusion Across a Membrane
5.2K. 1M views 2 years ago. Emig LV - Una Noche (Official Video) Directed By Max Fuerst Connect with me on social media: .more. Emig LV - Una Noche (Official Video) Directed By Max Fuerst.
Therefore, the discovery of mitochondrial ion channels influencing ion permeability through the membrane has defined a new dimension of the function of ion channels in different cell types, .

dior 637
In this review, we critically discuss the intracellular regulatory factors that affect channel activity in the inner membrane of mitochondria and, indirectly, contribute to cell death. .The main types of stimuli that are known to cause ion channels to open are a change in the voltage across the membrane (voltage-gated channels), a mechanical stress (mechanically gated channels), or the binding of a ligand .The field of mitochondrial ion channels has recently seen substantial progress, including the molecular identification of some of the channels. An integrative approach using genetics, .
The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel
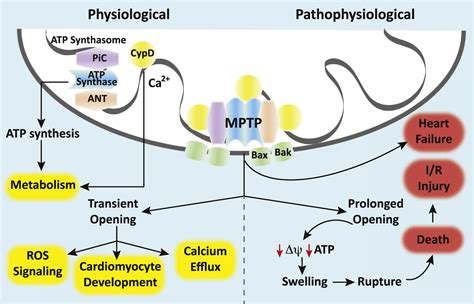
The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP). The pore-forming and ATP-binding subunits of a mitochondrial protein complex that mediates ATP-dependent potassium currents are identified and characterized, revealing .
The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP). After a brief .Emerging evidence indicates that mitochondrial ion channels activated by reactive oxygen species can induce a mitochondrial "critical" state, which can scale to cause electrical and contractile . This volume of the Annual Review of Biochemistry contains three reviews on membrane channel proteins: the first by Szczot et al., titled The Form and Function of PIEZO2; . Channels can be "gated" open by many mechanisms including ligand binding, change in membrane potential, lipid interactions, and mechanical stress. Opening a channel to .
The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel
Mitochondrial channels: ion fluxes and more
Therefore, the discovery of mitochondrial ion channels influencing ion permeability through the membrane has defined a new dimension of the function of ion channels in different cell types, mainly linked to the important tasks that mitochondrial ion channels perform in cell life and death.

In this review, we critically discuss the intracellular regulatory factors that affect channel activity in the inner membrane of mitochondria and, indirectly, contribute to cell death. These factors include various ligands, kinases, second messengers, and lipids.
The main types of stimuli that are known to cause ion channels to open are a change in the voltage across the membrane (voltage-gated channels), a mechanical stress (mechanically gated channels), or the binding of a ligand (ligand-gated channels).
The field of mitochondrial ion channels has recently seen substantial progress, including the molecular identification of some of the channels. An integrative approach using genetics, electrophysiology, pharmacology, and cell biology to clarify the roles of these channels has thus become possible.The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP). The pore-forming and ATP-binding subunits of a mitochondrial protein complex that mediates ATP-dependent potassium currents are identified and characterized, revealing the role of this channel in.The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP). After a brief historical introduction, we cover the key regulatory features of the PTP and provide a critical assessment of putative protein components that have been tested .
Emerging evidence indicates that mitochondrial ion channels activated by reactive oxygen species can induce a mitochondrial "critical" state, which can scale to cause electrical and contractile dysfunction of the cardiac cell and, ultimately, the whole heart. This volume of the Annual Review of Biochemistry contains three reviews on membrane channel proteins: the first by Szczot et al., titled The Form and Function of PIEZO2; the second by Ruprecht & Kunji, titled Structural Mechanism of Transport of Mitochondrial Carriers; and the third by Mc .
Channels can be "gated" open by many mechanisms including ligand binding, change in membrane potential, lipid interactions, and mechanical stress. Opening a channel to ion flow allows quick passage of information (in this case an electrical signal) into the cell, leading to quick cellular responses.Therefore, the discovery of mitochondrial ion channels influencing ion permeability through the membrane has defined a new dimension of the function of ion channels in different cell types, mainly linked to the important tasks that mitochondrial ion channels perform in cell life and death.
In this review, we critically discuss the intracellular regulatory factors that affect channel activity in the inner membrane of mitochondria and, indirectly, contribute to cell death. These factors include various ligands, kinases, second messengers, and lipids.The main types of stimuli that are known to cause ion channels to open are a change in the voltage across the membrane (voltage-gated channels), a mechanical stress (mechanically gated channels), or the binding of a ligand (ligand-gated channels).The field of mitochondrial ion channels has recently seen substantial progress, including the molecular identification of some of the channels. An integrative approach using genetics, electrophysiology, pharmacology, and cell biology to clarify the roles of these channels has thus become possible.
The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP).
Mitochondrial Ion Channels: Gatekeepers of Life and Death
The pore-forming and ATP-binding subunits of a mitochondrial protein complex that mediates ATP-dependent potassium currents are identified and characterized, revealing the role of this channel in.The mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) is a permeability increase of the inner mitochondrial membrane mediated by a channel, the permeability transition pore (PTP). After a brief historical introduction, we cover the key regulatory features of the PTP and provide a critical assessment of putative protein components that have been tested .Emerging evidence indicates that mitochondrial ion channels activated by reactive oxygen species can induce a mitochondrial "critical" state, which can scale to cause electrical and contractile dysfunction of the cardiac cell and, ultimately, the whole heart. This volume of the Annual Review of Biochemistry contains three reviews on membrane channel proteins: the first by Szczot et al., titled The Form and Function of PIEZO2; the second by Ruprecht & Kunji, titled Structural Mechanism of Transport of Mitochondrial Carriers; and the third by Mc .
Mitochondrial Ion Channels of the Inner Membrane and Their
Saturday 8:00am - 6:00pm. Get the motorcycle of your dreams with help from our financing department at Red Rock Harley-Davidson® Get financed today when you visit our dealership in Las Vegas, NV!
mitopoiesi chanel|Mitochondrial channels: ion fluxes and more